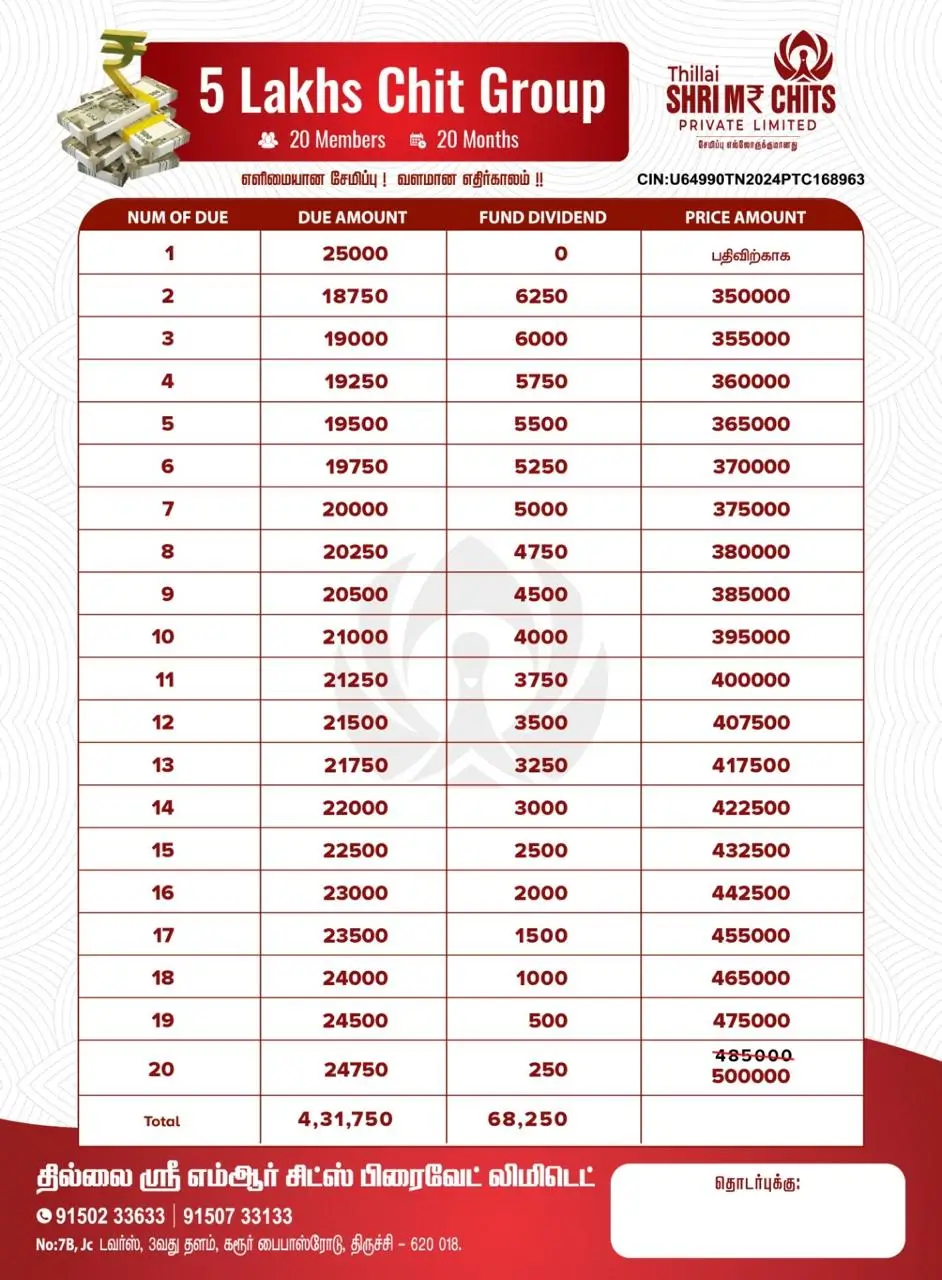
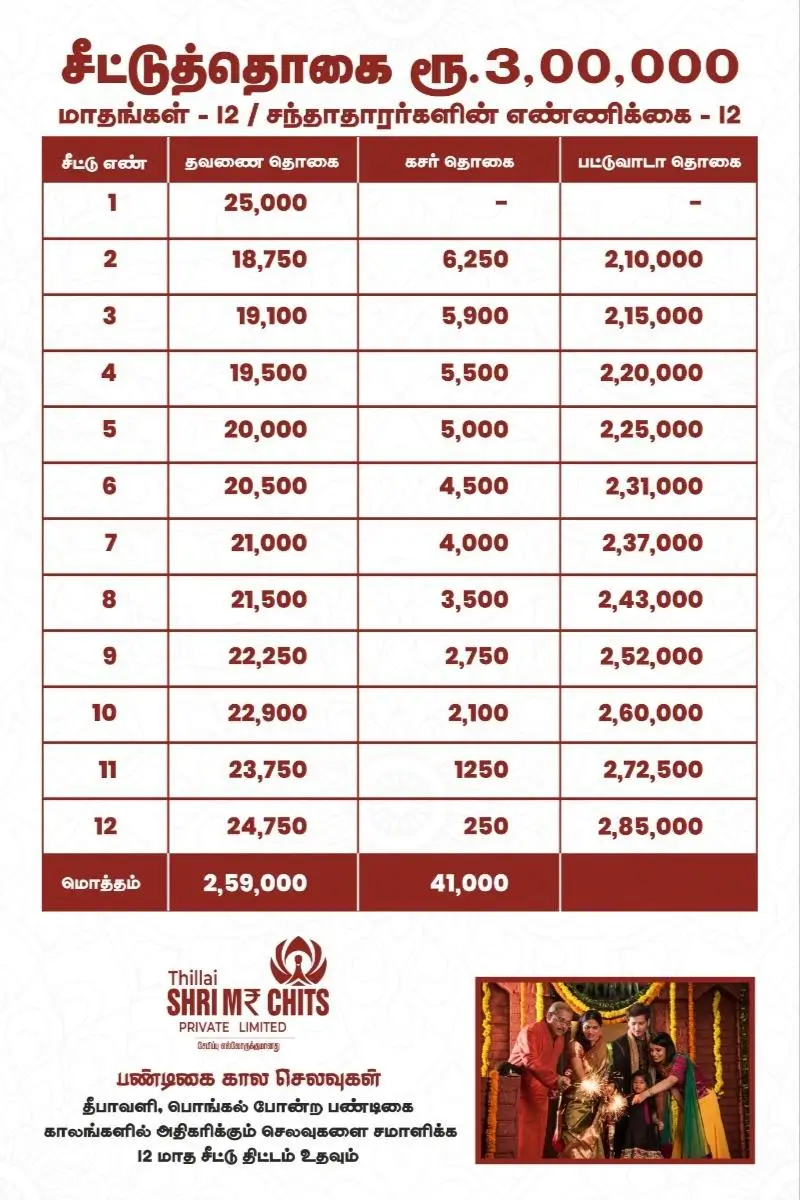
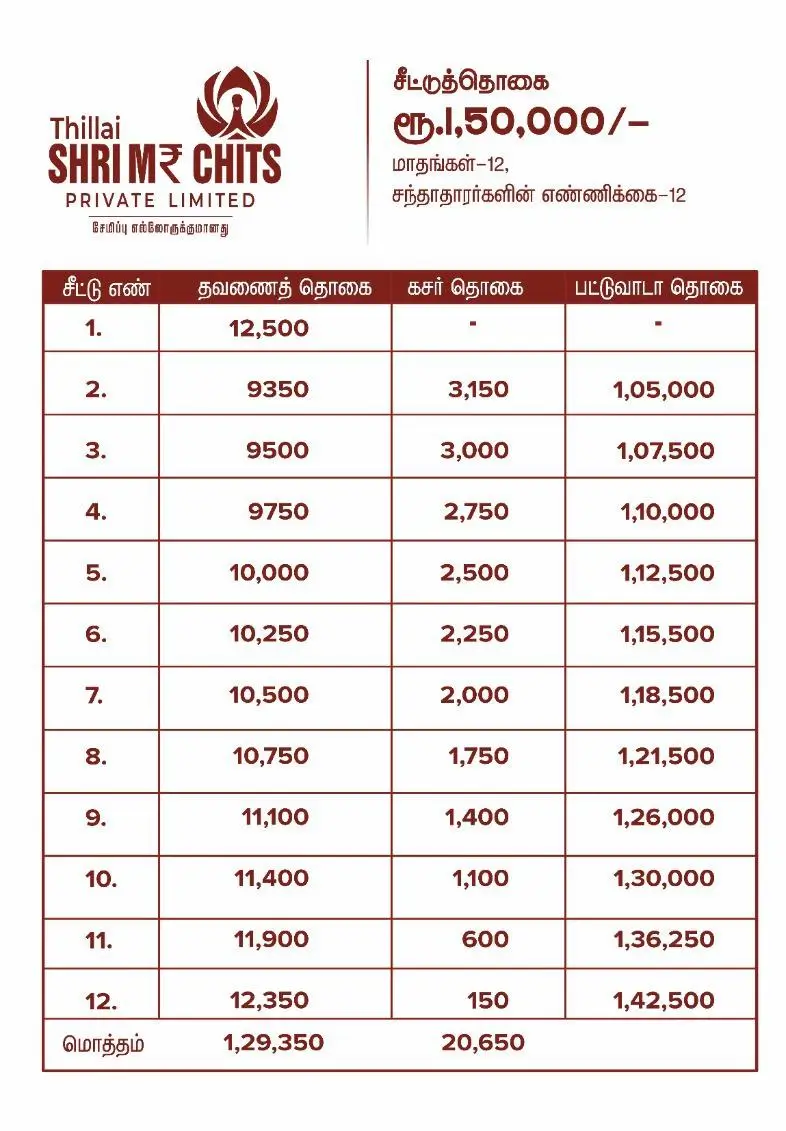
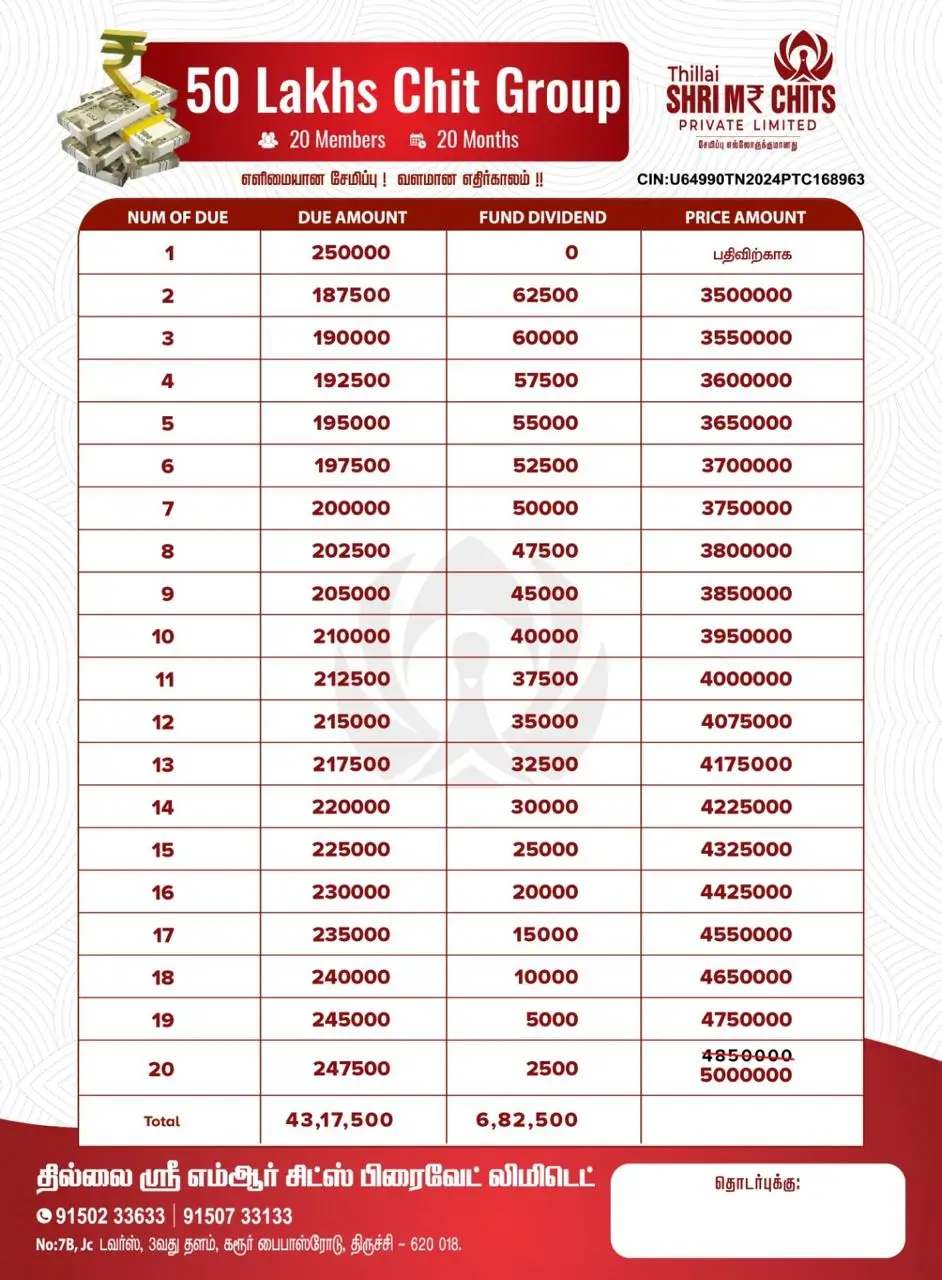
Managing money wisely is a skill that impacts nearly every aspect of life. Whether you are a student stepping into financial independence, a young professional navigating bills, or someone looking to secure a stable future, personal finance plays a critical role in achieving stability and freedom.
For beginners, personal finance can feel overwhelming. Terms like “budgeting,” “investing,” and “credit management” often sound complicated. But at its core, personal finance is about making conscious decisions about how you earn, spend, save, and grow your money.
This guide breaks down the essentials of personal finance, with a focus on the benefits of each step. By understanding these fundamentals, you can build strong financial habits that create long-term security and peace of mind.
Why Personal Finance Matters
Benefits of learning personal finance early
Financial Security
You are better prepared for emergencies.
Independence
You avoid relying on others for financial support.
Opportunity
Savings and investments give you the flexibility to pursue goals like travel, education, or business.
Peace of Mind
Money management reduces stress and helps you focus on other areas of life.
Step 1: Understanding Income and Expenses
The foundation of personal finance is knowing where your money comes from and where it goes.
Tracking Income
Your income includes salary, freelance earnings, side hustles, rental income, or any other source of cash flow. Knowing your total income helps you plan realistically
Tracking Expenses
- Fixed expenses: Rent, utilities, loan repayments.
- Variable expenses: Food, entertainment, shopping.
- Discretionary spending: Non-essentials like vacations, gadgets, or luxury items.
-
Benefit: When you track expenses, you identify wasteful spending and uncover opportunities to save more.
Step 2: Create a Budget
Budgeting is the roadmap for your money. Without it, money slips away unnoticed.
Methods of Budgeting
- 50/30/20 Rule: 50% of income for needs, 30% for wants, 20% for savings.
- Zero-Based Budget: Assign every rupee a purpose so nothing is wasted.
- Envelope System: Allocate cash into envelopes for categories like food, bills, and entertainment.
Benefits of budgeting:
- You stay in control of your spending.
- You save consistently without thinking too much about it.
- You avoid overspending and accumulating unnecessary debt.
Step 3: Build an Emergency Fund
Life is unpredictable. Medical bills, job loss, or sudden repairs can strike at any time. An emergency fund ensures you do not need to borrow money when unexpected costs arise.
How to Build It
- Start small with a goal of one month’s expenses.
- Gradually increase to cover 3–6 months.
- Keep it in a high-interest savings account for easy access.
Benefits of an emergency fund:
- Reduces stress during financial crises.
- Keeps you from relying on high-interest loans or credit cards.
- Provides a sense of security and stability.
Step 4: Manage Debt Wisely
Debt is one of the biggest obstacles to financial freedom. While some debts like home loans can be useful, high-interest debt such as credit cards can quickly spiral out of control.
Strategies for Debt Management
- Debt Avalanche: Pay off high-interest debt first to save money on interest.
- Debt Snowball: Pay off the smallest debt first to build motivation.
- Avoid New Debt: Focus on living within your means.
Benefits of managing debt:
- More disposable income for savings and investments.
- Improved credit score, making future borrowing cheaper.
- Greater financial freedom and reduced stress.
Step 5: Save for Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
Saving money is about preparing for the future while still enjoying life in the present.
Types of Savings
- Short-Term Savings: For goals like vacations, festivals, or buying new gadgets.
- Long-Term Savings: For milestones like higher education, marriage, or retirement.
Benefits of saving money:
- Helps you achieve goals without financial strain.
- Creates discipline in spending.
- Builds wealth and financial independence over time.
Step 6: Start Investing Early
Savings alone are not enough to grow wealth. Inflation reduces the value of money over time, which is why investing is essential.
Beginner-Friendly Investments
- Fixed Deposits: Low-risk and safe returns.
- Mutual Funds & SIPs: Diversified and easy to start with small amounts.
- Stocks & ETFs: Higher growth potential for long-term wealth.
- Retirement Accounts (PF, NPS, IRAs): Designed for secure retirement savings.
Benefits of investing early:
- Compound interest grows your money exponentially.
- Helps you achieve long-term goals faster.
- Builds passive income for financial freedom.
Step 7: Improve Your Credit Score
A credit score reflects how responsible you are with money and borrowing. A good score gives you access to loans with lower interest rates and higher approval chances.
How to Build Good Credit
- Pay bills and EMIs on time.
- Keep credit card usage below 30% of your limit.
- Avoid taking on unnecessary loans.
Benefits of a good credit score:
- Easier access to loans for homes or cars.
- Lower interest rates, saving you money.
- Better financial reputation with lenders.
Step 8: Use Financial Tools and Apps
Technology makes managing personal finance much easier.
Useful Tools
- Expense Trackers: Mint, YNAB, or Walnut for monitoring spending.
- Budgeting Apps: Goodbudget, PocketGuard.
- Investment Platforms: Groww, Zerodha, or Robinhood for easy investing.
- Automated Savings Apps: Round-up apps that save your spare change.
Benefits of financial tools:
- Simplify money management.
- Provide clear insights into financial habits.
- Keep you accountable toward your goals.
Step 9: Focus on Continuous Learning
Personal finance is not a one-time lesson. As your income grows and life changes, your financial strategies must also evolve. Reading books, attending workshops, or following financial experts can deepen your knowledge.
Benefits of financial learning:
- Keeps you updated on new saving and investment opportunities.
- Helps you avoid financial mistakes.
- Encourages smarter and more confident decision-making.
Step 10: Adopt the Right Mindset
Finally, personal finance is about mindset as much as it is about money. Building good habits and discipline ensures long-term success.
Key Mindset Shifts
- Think long-term instead of short-term gratification.
- Focus on needs versus wants.
- Prioritize experiences and security over excessive consumption.
Benefits of a money-conscious mindset:
- Greater control over your financial future.
- Ability to make confident choices without regret.
- Long-lasting peace of mind and independence.
Conclusion
Personal finance is not just about money—it is about building a life that feels secure, free, and aligned with your goals. For beginners, the journey starts with understanding income and expenses, creating a budget, building an emergency fund, managing debt, and saving consistently. From there, investing, improving credit, and using financial tools help accelerate progress.
The greatest benefit of personal finance is freedom. By making conscious decisions about money, you gain independence, reduce stress, and create opportunities for yourself and your family. Start small, stay consistent, and over time, these habits will transform your financial future.